Welcome to RnD Marketing’s guide to technical SEO. Dive into essential strategies for optimizing your website’s performance in search engine rankings. Whether you’re a beginner or an expert, this guide offers valuable insights to enhance your site’s technical prowess. Let’s begin your journey to mastering technical SEO!
What are we going to cover today?
What is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO is about optimizing a website’s backend structure to improve its ranking and visibility in search engines. It’s different from on-page SEO, which focuses on content, SEO writing, and keywords. Technical SEO ensures that search engines can effectively crawl, index, and interpret a site. This includes optimizing site speed, ensuring mobile-friendliness, setting up secure connections with HTTPS, and fixing crawl errors like broken links. It also involves managing sitemaps, using canonical tags to avoid duplicate content, and implementing structured data for better context understanding by search engines. Essentially, technical SEO not only helps in better indexing by search engines but also enhances the overall user experience, leading to better site performance in search results.
The Pillars of Technical SEO
In the world of SEO, technical optimization is not just a one-time task, but an ongoing process that ensures your website is both discoverable and navigable by search engines. Understanding and implementing the pillars of technical SEO is crucial for anyone aiming to boost their site’s visibility and user experience. Let’s delve into these core aspects, essential for anyone learning more about technical SEO.
Site Indexability
Ensuring your website is accessible to search engine crawlers is the base of technical SEO. If search engines can’t find and crawl your site, it’s almost as if it doesn’t exist in the digital world. The key is to make your website easily navigable for these crawlers.
One primary method for checking site accessibility is the use of tools like Google Search Console. It allows you to see your website as Google does. Let’s see an example of what it looks like:
You can check for crawl errors, view the pages indexed by Google, and even submit sitemaps. Ensuring your robots.txt file is correctly configured is also crucial, as it informs crawlers which parts of your site should or should not be crawled – more on that later.
Site Structure and Navigation
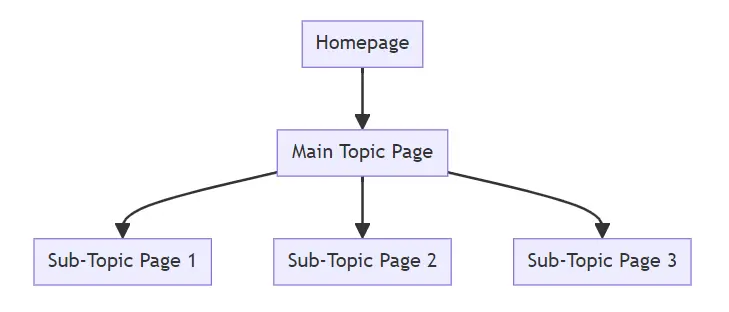
An intuitive site structure is not only beneficial for users but also for search engines. A well-organized website with clear navigation helps search engines understand your site’s hierarchy and content priority, which in turn can impact your search rankings.
To achieve an SEO-friendly site structure, start with a logical hierarchy in your menu design. Every page should be reachable through a few clicks from the home page. Internal linking plays a crucial role here. By strategically using internal links, you guide visitors and search engines through your site, increasing the reach and visibility of even deeper pages. Remember, a good internal linking structure also distributes page authority throughout the site, boosting the SEO performance of individual pages.
Mobile Optimization
With the advent of mobile-first indexing by Google, optimizing your website for mobile devices has never been more important. This means Google predominantly uses the mobile version of the content for indexing and ranking. As mobile usage continues to rise, having a mobile-optimized website is a key factor in your technical SEO strategy.
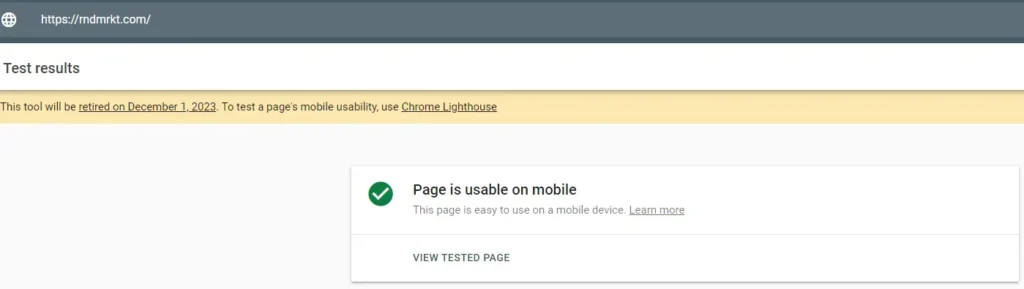
To ensure mobile optimization, your website should feature a responsive design that adjusts content according to the screen size. Additionally, page loading speed on mobile devices is a critical factor. Tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test (which will be retired on December 1, 2023) or Chrome Lighthouse, can help you evaluate your site’s performance on mobile devices and provide recommendations for improvement. Remember, a mobile-optimized site not only caters to search engine requirements but also provides a better user experience, leading to higher engagement and conversion rates.
Let’s take a look at a mobile-friendly test we ran on our website using the Mobile-Friendly Test:
By focusing on these pillars of technical SEO, you establish a strong foundation for your website’s visibility and user experience. Whether you’re handling SEO in-house or utilizing professional technical SEO services, these strategies are instrumental in navigating the complex landscape of search engine optimization.
Speed Optimization Techniques
The speed of your website is a critical factor for success. Speed optimization is not just about improving user experience; it’s also a key driver for SEO performance. Slow-loading websites can lead to high bounce rates and low user engagement, directly impacting your site’s visibility and ranking on search engines. Let’s explore the techniques and tools necessary to boost your website’s speed.
Importance of Page Speed
Page speed significantly impacts both the user experience and your website’s SEO performance. A fast-loading website holds users’ attention, reduces bounce rates, and encourages more in-depth interaction with your content, which search engines interpret as a sign of quality and relevance. On the SEO front, Google has explicitly mentioned page speed as a ranking factor, especially with its mobile-first indexing approach.
Tools for Measuring Page Speed:
- Google PageSpeed Insights: Offers comprehensive insights into your website’s performance on both desktop and mobile, along with actionable recommendations for improvement.
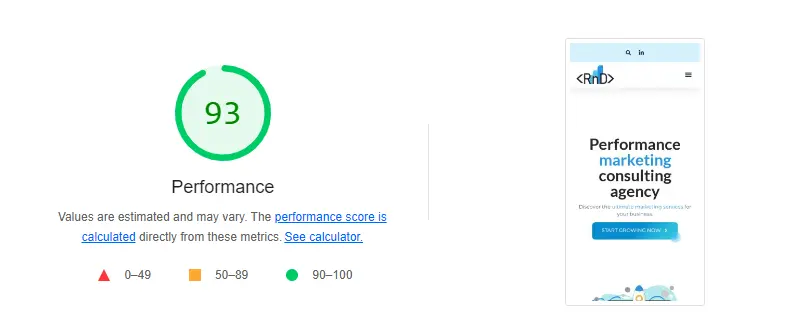
- GTmetrix: Provides detailed reports on your site’s speed performance, including YSlow scores, page load time, total page size, and the number of requests. Here’s a report of RnD Marketing’s homepage on GTmetrix.
- WebPageTest: Allows for more advanced testing from multiple locations and browsers, detailed optimization suggestions, and visualizations of page load.
There are other tools available, but we recommend using PageSpeed Insights as it’s directly connected to Google.
Interesting read: Core Web Vitals case study
Enhancing Website Performance
Optimizing the performance of your website involves several technical strategies that can significantly improve loading times.
Tips for Optimizing Images, CSS, and JavaScript:
- Compress Images: Large image files can dramatically slow down your website. Use tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim for efficient image compression without losing quality.
- Next-gen Image Formats: Use image formats like WebP or AVIF that offer better compression while maintaining the same image quality.
- Minify CSS and JavaScript: Minification is the process of removing unnecessary characters (like whitespace) from code to decrease its size and improve load time.
- Use CSS Sprites: Combine multiple images into a single image file with CSS sprites, reducing the number of HTTP requests. This is an advanced technique.
Leveraging Browser Caching and Content Delivery Networks (CDNs):
- Browser Caching: Store parts of your website in the user’s browser so that it doesn’t have to be reloaded each time they visit your site. This can be configured through your website’s .htaccess file. Otherwise, you can use plugins like WP Rocket.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Distribute your content across multiple, geographically diverse servers using a CDN. This reduces the distance between the user and the server, speeding up the loading process. Popular CDNs include Cloudflare (which we are using) and Amazon CloudFront.
Advanced Speed Optimization Techniques Cheat Sheet
| Optimization Technique | Description | Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Compress Images | Reduces image file size to speed up loading without sacrificing quality. | TinyPNG, ImageOptim |
| Next-gen Image Formats | Utilize modern image formats for better compression and quality. | WebP, AVIF |
| Minify CSS and JavaScript | Removes unnecessary characters from code to decrease file size. | CSS and JavaScript minification tools like the WP Rocket plugin |
| Use CSS Sprites | Combines multiple images into a single file, reducing HTTP requests. | CSS sprite generators |
| Browser Caching | Stores website data in the user’s browser to avoid reloading for returning visitors. | .htaccess configuration, WP Rocket plugin |
| Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) | Distributes content across various servers to reduce load time. | Cloudflare, Amazon CloudFront |
This table provides a concise overview of various techniques that we discussed and can be employed to optimize the speed of a website. Each method offers a unique approach to enhancing website performance, from image compression to leveraging CDNs. By implementing these strategies, you can significantly improve your site’s loading time, which is crucial for both user experience and SEO.
Advanced Indexing Strategies
To maximize the visibility of your website in search engine results, mastering some advanced indexing strategies is essential. This section of our guide delves into the nuances of creating and optimizing sitemaps, and effective ways to address common indexing issues. These strategies are key to ensuring search engines not only find all your important pages but also understand how to prioritize and display them.
Mastering Sitemaps
An XML sitemap is a roadmap of your website that guides search engines to all your important pages. Creating an XML sitemap involves listing the URLs of your site along with additional metadata about each URL (like when it was last updated, how often it changes, and its importance relative to other URLs).
Tools for Sitemap Creation:
- Online Sitemap Generators: Tools like XML-Sitemaps.com or Screaming Frog SEO Spider can automatically generate sitemaps for your website.
- Content Management Systems (CMS): Platforms like WordPress often have plugins, like Yoast SEO, that include sitemap generation functionality. Here’s an image of how the Yoast SEO sitemap looks on our website:
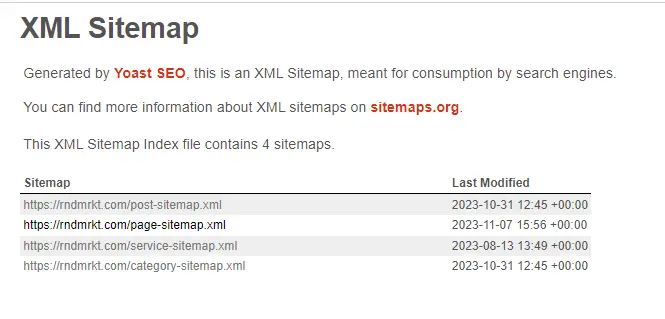
Submitting Sitemaps to Search Engines:
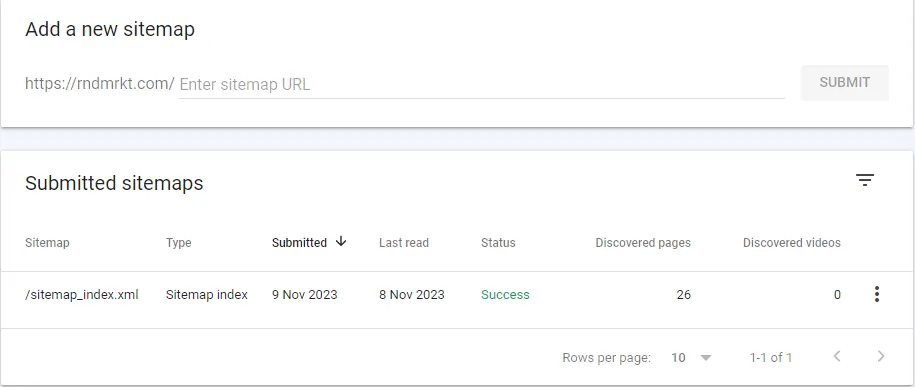
Once your sitemap is ready, submit it to search engines like Google and Bing. This can be done through their respective Webmaster Tools (Google Search Console for Google and Bing Webmaster Tools for Bing).
Steps for Submitting a Sitemap:
- Sign in to Google Search Console or Bing Webmaster Tools.
- Select the property (website) you want to manage.
- Locate the ‘Sitemaps’ section and submit your XML sitemap URL.
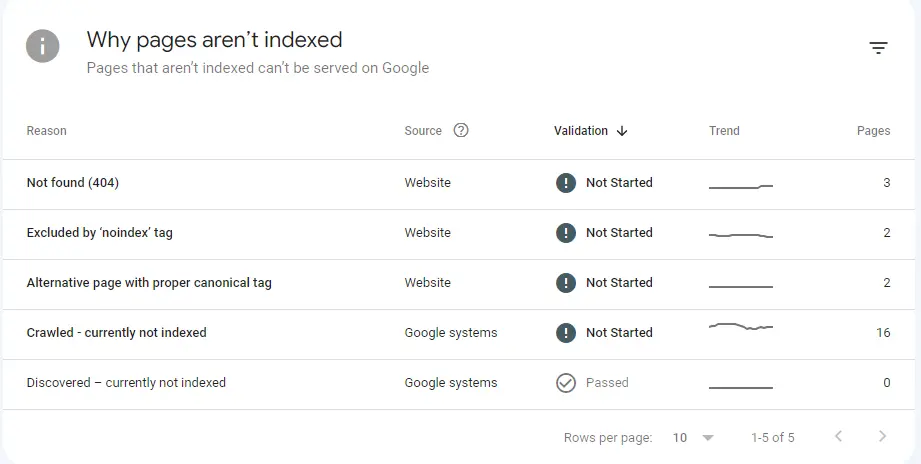
Handling Indexing Issues
Common indexing issues include having non-indexable pages (pages blocked from search engines) and duplicate content. Tools like Google Search Console can help identify these problems by showing crawl errors or duplicate content warnings.
Solutions for Indexing Issues:
- Audit Your Site: Regularly check for crawl errors or indexing issues in Google Search Console. Here’s
- Fix Duplicate Content: Ensure each page on your site has unique content and proper canonical tags.
Using Robots.txt and Meta Tags Effectively:
The robots.txt file and meta tags are powerful tools for managing how search engines crawl and index your site.
- Robots.txt: This is a text file located in the root directory of your site that tells search engines which pages or sections should not be crawled. Attached below is an example of how the robots.txt file generated by Yoast SEO looks like on our website:
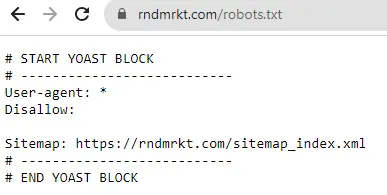
- Meta Tags: Specific HTML tags (like ‘noindex’) can be used to prevent search engines from indexing certain pages. A good example would be login pages, different policy pages, feeds, tags, categories, and more.
Checklist: Effective Indexing Strategies
☑ Create and regularly update XML sitemaps.
☑ Submit sitemaps to major search engines.
☑ Monitor for indexing issues using tools like Google Search Console.
☑ Resolve duplicate content and non-indexable pages.
☑ Utilize robots.txt and meta tags strategically.
By implementing these advanced indexing strategies, you can significantly improve your website’s visibility and ranking in search engine results, ensuring that your valuable content gets the attention it deserves.
Security and User Experience
In the world of technical SEO, security and user experience play important roles. This section will explore how securing your website with HTTPS can boost your SEO efforts, and why focusing on user experience is essential for higher engagement and conversion rates.
The Role of HTTPS
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is the secure version of HTTP, where communications between your browser and the website are encrypted. Implementing HTTPS is crucial for protecting your site’s data integrity and confidentiality. From an SEO perspective, Google has confirmed HTTPS as a ranking signal. Websites with HTTPS are often perceived as more trustworthy by users, leading to higher engagement rates.
Steps to Migrate to HTTPS:
- Purchase an SSL Certificate: You can buy an SSL certificate from a trusted certificate authority (CA) or get a free one from Let’s Encrypt.
- Install and Activate the SSL Certificate: Your hosting provider can often assist with this step. In our case, we are using Hostinger which offers a free SSL installation.
- Update Your Website to Use HTTPS: Ensure that all your web pages, resources, and links use the HTTPS protocol.
- Set Up 301 Redirects: Use 301 redirects to redirect all HTTP pages to HTTPS to maintain SEO rankings. You can do so automatically through cPanel or any other control panel you are using.
- Update Your Sitemap and Robots.txt File: Ensure they reflect the HTTPS version of your site. If you are using plugins to generate those, it’ll most likely update automatically.
Enhancing User Experience
A website that’s easy to navigate and enjoyable to use can significantly increase user engagement, lower bounce rates, and improve conversion rates. Search engines favor websites that offer a good user experience, making this a crucial factor in SEO.
Strategies for Improving Site Navigation and Content Layout:
- Clear and Logical Navigation: Ensure that your site’s menu is intuitive and helps users find what they’re looking for quickly.
- Responsive Design: Your site should be easily viewable and navigable on all devices, including desktops, tablets, and smartphones. Here’s an example of how our website looks like on mobile devices:

- Optimized Page Load Speed: As discussed earlier, faster pages enhance user experience.
- Use of Visual Hierarchies: Organize content in a way that guides visitors through your pages naturally.
- Accessibility: Make sure your site is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities by keeping a good contrast ratio, naming buttons, and more.
User Experience Checklist:
☑ Intuitive and clear navigation structure.
☑ Responsive design for multi-device compatibility.
☑ Fast-loading web pages.
☑ Organized content with a clear visual hierarchy.
☑ Accessibility features for an inclusive user experience.
By focusing on HTTPS for security and prioritizing user-friendly design, you can create a website that not only ranks well in search engines but also delights and retains your visitors. These elements are fundamental in building a successful online presence that resonates with both search engines and users.
Structured Data and Rich Snippets
Structured data and rich snippets are powerful tools in the technical SEO toolkit. They enhance the way your website communicates with search engines, providing clear context about your content. This section explores the essentials of using structured data and the significant impact of rich snippets on your search visibility.
Understanding Structured Data
Structured data refers to a standardized format for providing information about a webpage and classifying the page content. This is often done using Schema markup, a vocabulary of code (semantic vocabulary) that helps search engines understand the context of your content. By implementing Schema, you can enhance your website’s visibility and improve the way your pages are represented in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Benefits of using structured data include:
- Enhanced search visibility.
- Better understanding by search engines.
- Potential to appear in rich results, improving click-through rates.
Tools for Implementing Structured Data:
- Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper: An interactive tool to generate structured data markup for your website. Access here.
- Schema.org: The official resource for Schema markup vocabulary.
- Testing tools like Google’s Rich Results Test: To validate your structured data. Access here.
Example of Structured Data Using Schema Markup:
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "HowTo",
"name": "How to Do SEO: A Beginner's Guide",
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "Alex Smith"
},
"datePublished": "2023-11-13",
"description": "A comprehensive guide for beginners on how to optimize your website for search engines, covering everything from keyword research to technical SEO.",
"step": [
{
"@type": "HowToStep",
"name": "Keyword Research",
"text": "Identify relevant keywords that your target audience is searching for."
},
{
"@type": "HowToStep",
"name": "On-Page SEO",
"text": "Optimize individual pages of your website with the selected keywords."
},
{
"@type": "HowToStep",
"name": "Technical SEO",
"text": "Ensure your website's technical setup helps search engines effectively crawl and index your site."
},
{
"@type": "HowToStep",
"name": "Link Building",
"text": "Improve your website's authority by gaining high-quality backlinks."
}
],
"estimatedCost": {
"@type": "MonetaryAmount",
"currency": "USD",
"value": "0"
},
"totalTime": "PT10H"
}
</script>This example shows how you can use Schema markup for a guide on SEO. It outlines various steps involved in the SEO process, such as keyword research, on-page SEO, technical SEO, and link building. This structured data is designed to help search engines understand and present the content of your guide in a rich, informative format in the search results.
Rich Snippets
Rich snippets are enhanced search results with additional information displayed, like ratings, images, or other relevant details. To earn these snippets, you must implement structured data correctly on your website.
Examples of Different Types of Rich Snippets:
- Product Snippets: Display price, availability, and review ratings for products.
- Recipe Snippets: Show a recipe’s photo, ratings, cooking time, and calorie count.
- Review Snippets: Highlight user reviews and ratings.
- Event Snippets: Provide details of an event, such as date, location, and time.
- FAQ Snippets: Used to showcase frequently asked questions directly in search results, but now doesn’t for most websites.
Rich snippets make your content stand out in SERPs, leading to higher click-through rates and better user engagement. The key is to use structured data effectively and ensure it’s accurately implemented across your website. By doing so, you elevate your content’s visibility and appeal in the eyes of both search engines and users.
Addressing Duplicate Content
Duplicate content can pose significant challenges in SEO, potentially diluting your site’s relevance and splitting link equity. In this section, we’ll explore effective strategies to identify and address duplicate content, and the role of canonical tags in maintaining content uniqueness.
Identifying Duplicate Content
Detecting duplicate content involves identifying pages with identical or very similar content. Here are some tools and methods to assist you:
- Google Search Console: Check the ‘Pages’ report for insights on duplicate content issues. Here’s an example of a possible duplicate issue:
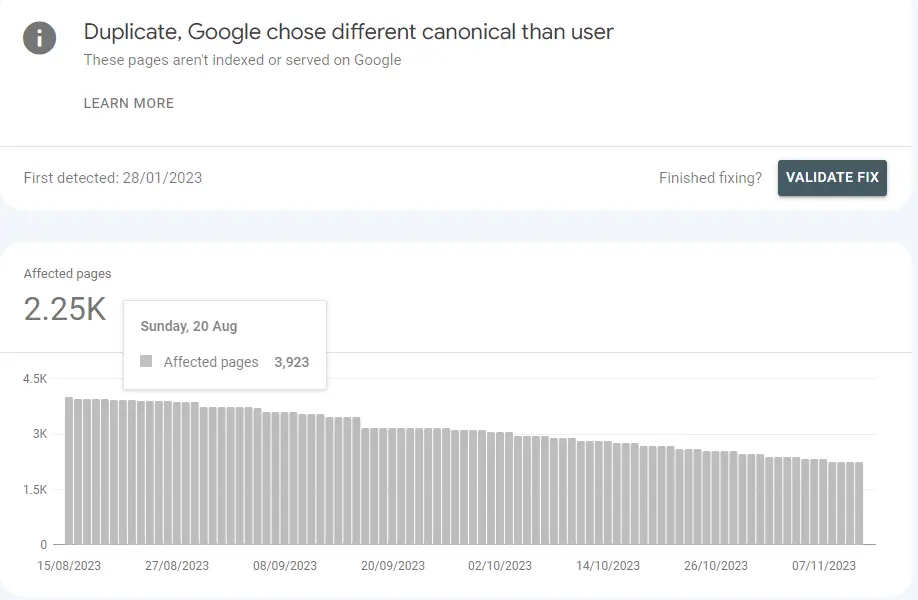
- Plagiarism Checkers: Tools like Copyscape or Siteliner can scan your website for duplicate content across the web.
- SEO Tools: Platforms like SEMrush or Ahrefs offer site audit features that can detect duplicate content within your website.
Strategies for Handling Similar Content Across Pages:
- Consolidate Similar Pages: If multiple pages serve the same purpose, consider merging them into a single, comprehensive page.
- Use 301 Redirects: Redirect duplicate pages to the primary page to consolidate link equity and relevance.
- Vary Your Content: Ensure that each page has unique content, especially in meta tags, headings, and body content.
- Canonicalize Pages: This is especially useful for E-commerce websites that use the same content for a few variations of the same product, while each variation has a different URL. We are going to cover it in-depth now!
Canonical Tags
A canonical tag (rel=”canonical”) is an HTML element that helps prevent duplicate content issues by specifying the “preferred” version of a web page. It’s essential for SEO because it tells search engines which version of a URL you want to appear in search results.
Implementing Canonical Tags:
- Choose the Preferred URL: Decide which version of a duplicate or similar page is the most relevant or comprehensive.
- Insert the Canonical Tag: Place the canonical tag in the
<head>section of the HTML of the duplicate pages, pointing to the preferred URL.htmlCopy code<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.example.com/preferred-page" /> - Be Consistent Across Internal Linking: Ensure that internal links point to the URL designated as the canonical version.
Duplicate Content Solutions:
| Issue | Tool/Method | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Duplicate Content | SEO Site Audit Tools | Merge, Redirect, or Canonicalize |
| External Content Duplication | Plagiarism Checkers | Modify Content to be Unique |
| Similar Content on Multiple Pages | Manual Review/SEO Tools | Consolidate or Vary Content |
By properly identifying and addressing duplicate content and effectively using canonical tags, you can enhance your website’s SEO performance, ensuring that each page uniquely contributes to your site’s overall search visibility.
Core Web Vitals and Site Health
A key component of technical SEO in today’s digital landscape is understanding and optimizing Core Web Vitals. These are a set of specific factors that Google considers important in a webpage’s overall user experience. Coupled with regular technical SEO audits, these elements are vital in maintaining and improving your site’s health and performance.
Understanding Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals consist of three main metrics: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). These metrics measure the loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability of a page, respectively.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures the time it takes for the largest content element on your page to load. A good LCP score is 2.5 seconds or faster.
- First Input Delay (FID): Measures the time from when a user first interacts with your site to the time when the browser is able to respond to that interaction. An ideal FID is less than 100 milliseconds.
Please note: FID will be replaced by INP in March 2024! - Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures how much visible content shifts on the page during loading. A CLS score of less than 0.1 is recommended.
Tools for Measuring and Improving Core Web Vitals:
- Google PageSpeed Insights: Provides insights into how well your site loads and offers suggestions for improvement. Visit here.
- Lighthouse: An open-source, automated tool by Google that audits the quality of web pages, including performance metrics.
- Web Vitals Chrome Extension: Offers a real-time report of the Core Web Vitals metrics for any webpage.
Soon, we will release a new article that covers Core Web Vitals optimization in-depth.
Regular Technical SEO Audits
Regular technical SEO audits are essential to identify and fix issues that could affect your site’s performance and search engine ranking. These audits help ensure your website aligns with best practices for SEO and provides an optimal user experience.
Recommended Tools and Practices for Continuous SEO Health Checks:
- SEO Auditing Tools: Platforms like SEMrush, Ahrefs, and Moz offer comprehensive site audit functionalities that highlight issues affecting your site’s SEO performance.
- Google Search Console: Use this tool to monitor your site’s performance in Google SERP, track Core Web Vitals, and check for crawling and indexing issues.
- Regular Monitoring: Schedule regular audits (weekly, monthly, or quarterly) to keep track of your website’s health. Pay special attention to site speed, mobile usability, and technical errors.
Checklist for Technical SEO Site Health:
☑ Regularly monitor Core Web Vitals scores.
☑ Conduct comprehensive SEO audits at regular intervals.
☑ Address technical issues such as broken links, crawl errors, and mobile usability.
☑ Update content and website structure as per the latest SEO best practices.
By focusing on Core Web Vitals and incorporating regular technical SEO audits into your digital strategy, you ensure that your website remains healthy, user-friendly, and well-optimized for search engines. This proactive approach is key to maintaining a strong online presence and achieving long-term success in the competitive digital landscape.
Multilingual SEO and Hreflang Tags
In an increasingly global online marketplace, optimizing your website for multiple languages is not just beneficial—it’s often essential. Multilingual SEO involves strategies to target audiences in different linguistic regions, ensuring that the right content reaches the right users. A crucial element of this is the correct implementation of hreflang tags, which help search engines understand language and regional targeting.
Optimizing for Multiple Languages
When you expand your website to cater to multiple languages, you open up new avenues for traffic and engagement. However, it requires strategic planning and execution.
Best Practices for Multilingual Websites:
- Accurate Translation and Localization: Ensure that content is not just translated but also localized to suit cultural nuances and regional dialects.
- Separate URLs for Different Language Versions: Use either subdirectories, domains, or subdomains to separate content in different languages. For example, use example.com/fr for French and example.com/es for Spanish versions. Here’s an example:
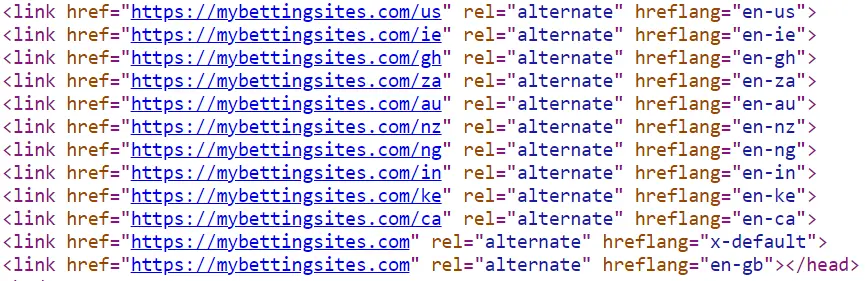
- Localized Keyword Research: Perform keyword research for each language to understand what your target audience in different regions is searching for.
- Consistent Brand Messaging: While adapting content for different languages, maintain the essence of your brand’s message.
Implementation and Validation of Hreflang Tags
Hreflang tags tell search engines which language and geographic target area a specific page targets. This ensures that users are directed to the version of your site most relevant to their language or region.
Steps for Hreflang Tag Implementation:
- Tag Placement: Place hreflang tags in the section of your HTML, or in the HTTP headers for non-HTML files.
- Use Correct Language Codes: Use the ISO 639-1 format for language and ISO 3166-1 Alpha 2 for country codes. For example, en-GB stands for English in Great Britain.
- Specify a Default Language: Use an x-default tag to indicate a default page when no other page is better suited for the user’s language or location.
Example of x-default hreflang usage:
<link rel="alternate" href="http://example.com" hreflang="x-default" />
<link rel="alternate" href="http://example.com/fr" hreflang="fr" />
<link rel="alternate" href="http://example.com/es" hreflang="es" />
Validating Your Hreflang Tags:
- Google Search Console: Use the ‘International Targeting’ report to check for errors in your hreflang tag implementation.
- Hreflang Tag Testing Tools: Tools like Aleyda Solis’s Hreflang Tags Generator and Checker can help you validate your hreflang tags.
By effectively optimizing for multiple languages and correctly implementing hreflang tags, you can significantly improve your site’s global reach and ensure that your content resonates with diverse audiences. This approach is key to successful international SEO and building a truly global online presence.
Conclusion
Mastering technical SEO is key to elevating your website’s performance and search engine ranking. At RnD Marketing, we understand the intricacies of this process, from optimizing for Core Web Vitals to implementing multilingual solutions. Our expertise and rich experience ensure your site is not just search-engine friendly but also delivers a superior user experience.
Trust RnD Marketing to navigate the complexities of technical SEO for you, transforming challenges into opportunities for your digital success. Choose us for a partnership where every detail is tailored to drive your online growth!
Frequently Asked Questions
Technical SEO involves optimizing the infrastructure and technical aspects of a website to improve its visibility and ranking in search engine results. It includes optimizing site speed, mobile-friendliness, indexing, and security.
Site speed is crucial because it affects user experience and is a Google ranking factor. Faster sites reduce bounce rates, improve user engagement, and are generally favored in search engine rankings.
You can check your website’s mobile-friendliness using tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test. This tool analyzes your site and reports if it has a mobile-friendly design.
Core Web Vitals are a set of specific factors Google considers important for a webpage’s overall user experience, including loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability. They’re important because they directly impact user experience and influence SEO rankings.
A sitemap is a file that lists all the pages of your website, making it easier for search engines to crawl and index your site. You can create a sitemap manually or use tools like XML-Sitemaps.com, or content management systems with built-in sitemap generators like WordPress with the Yoast SEO plugin.





